日本語で話そう。Jargonic is ready.
Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) systems often excel in lab conditions but struggle in real-world enterprise environments—especially when it comes to linguistically complex languages like Japanese. Unlike English, Japanese doesn’t use whitespace (the spaces between words in a sentence) to separate words, making Word Error Rate (WER) less relevant as a benchmark. Instead, Character Error Rate (CER) becomes the primary metric for evaluating transcription quality.
On top of that, Japanese blends three diverse writing systems-–hiragana, katakana, and kanji–, with hundreds of honorific structures, and shifting pronunciations based on context. For example, the word “three” sounds different when referring to people, flat objects, or animals. Combined with dense domain-specific jargon, these intricacies make Japanese one of the most challenging languages for ASR to master. With the release of Jargonic V2, aiOla continues to break through these barriers.
After setting new benchmarks in English, Spanish, French, and more, Jargonic V2 now leads in Japanese as well—delivering not just superior transcription accuracy, but also unmatched recall of specialized terms across industries like manufacturing, logistics, healthcare, and finance.
Going Beyond Transcription: Why Jargon Recall Matters
Most ASR models today are “universal scribes”—trained for broad transcription accuracy but unfit for recognizing the acronyms, product names, and technical terminology found in real-world enterprise settings. That’s where Jargonic stands apart.
Our proprietary Keyword Spotting (KWS) technology allows Jargonic to identify domain-specific terms without the need for retraining or manually curated vocab lists. Unlike traditional models, which may stumble when encountering niche or industry-specific words, Jargonic detects them in real-time—thanks to a context-aware, zero-shot learning mechanism deeply integrated into the ASR pipeline.
Benchmark Results: Jargonic vs. the Field
We tested Jargonic V2 on two Japanese datasets (both includes all three primary Japanese scripts kanji, hiragana, and katakana):
- CommonVoice v.13 – a standard dataset that tests general speech recognition capabilities.
- ReazonSpeech – Diverse set of natural Japanese speech, collected from terrestrial television streams.
Across both datasets, Jargonic outperformed Whisper v3, ElevenLabs, Deepgram, and AssemblyAI in key areas:
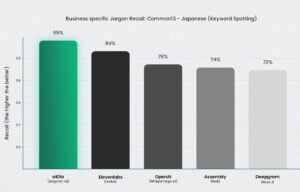
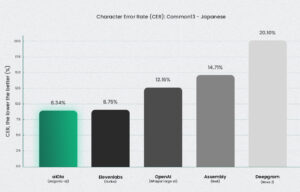
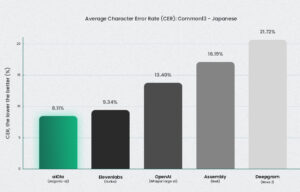
Jargonic delivered a 94.7% recall rate for domain-specific Japanese terms—meaning it correctly detected nearly all specialized jargon without training. No other model came close.
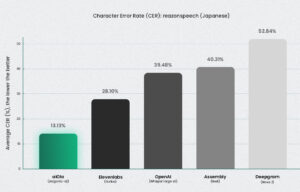
Even in natural, unstructured Japanese speech (Reazon dataset), Jargonic outperformed every other model—cutting character error rate (CER) in half or better.
Built for the Real World
These results aren’t just academic. They highlight a fundamental capability for enterprises operating in multilingual, jargon-heavy environments: the ability to capture accurate, structured data from spoken interactions—no matter the language, context, or complexity.
With Jargonic, speech becomes a reliable interface for enterprise AI—not just for transcription, but for real-time understanding and action.













