Imagine a world where factories operate with near-perfect efficiency, machines predict their own maintenance needs, and production lines adjust in real time to meet demand—welcome to smart manufacturing.
While it may not involve flying assembly robots (yet), this cutting-edge approach is revolutionizing the industry by integrating AI, IoT, automation, and data analytics to create smarter, faster, and more adaptable manufacturing systems. As businesses navigate an increasingly digital world, smart manufacturing isn’t just an advantage—it’s a necessity for staying competitive. So, what exactly is smart manufacturing, and why is it shaping the future of industry? Let’s dive in.
What Is Smart Manufacturing?
Smart manufacturing is at the root of creating more advanced, efficient manufacturing processes than more traditional means. It is the use of technologies, such as artificial intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoT), cloud computing, big data analytics, robotics, and automation to improve efficiency, productivity, and quality in manufacturing processes. It enables real-time data collection, analysis, and decision-making to optimize operations and reduce waste.
Smart manufacturing and Industry 4.0 go hand in hand, with the latter driving the integration of advanced technologies into manufacturing and transforming traditional analog systems into digital ones. As the fourth stage of industrial development, Industry 4.0 follows the progression from the First Industrial Revolution (mechanization), to mass production, to automation and electronics, and now to smart manufacturing, where AI, IoT, and data-driven decision-making define the future of industry.
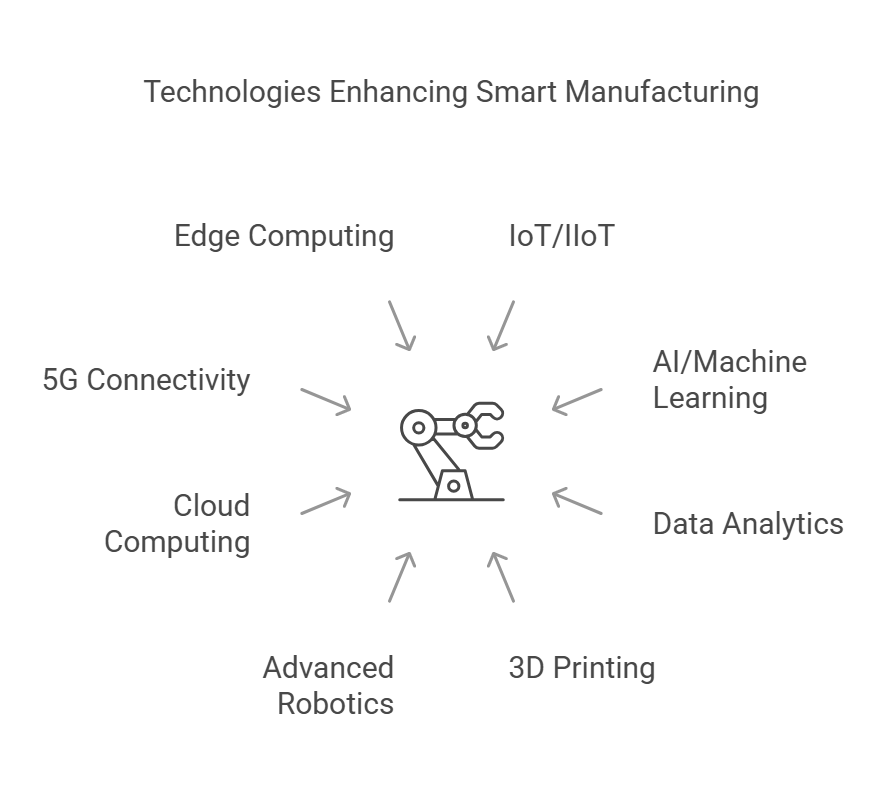
Smart Manufacturing Technologies
Let’s break down the main smart manufacturing technologies:
- IoT/IIoT: The Internet of Things (IoT) and its industrial counterpart (IIoT) connect machines, sensors, and systems to enable real-time monitoring and data-driven decision-making in manufacturing.
- AI / Machine Learning: Artificial intelligence and machine learning optimize production by predicting maintenance needs, improving quality control, and automating complex tasks.
- Data Analytics and AI: Advanced data analytics, powered by AI, helps manufacturers process vast amounts of information to identify patterns, enhance efficiency, and reduce waste.
- Additive Manufacturing with 3D Printing: 3D printing enables rapid prototyping, custom manufacturing, and reduced material waste by building components layer by layer.
- Advanced Robotics: Intelligent robots handle repetitive tasks with precision, improving productivity and workplace safety while working alongside human operators.
- Cloud Computing: Cloud-based platforms allow manufacturers to store, process, and analyze data remotely, ensuring seamless collaboration and scalability.
- 5G Connectivity: High-speed, low-latency 5G networks enhance communication between smart factory devices, enabling faster automation and real-time decision-making.
- Edge Computing: By processing data closer to the source, edge computing reduces latency and improves response times for critical manufacturing operations.
- Digital Twins: Virtual replicas of physical assets, known as digital twins, allow manufacturers to simulate, test, and optimize processes before implementing changes in the real world.
- Blockchain in the Supply Chain: Blockchain technology enhances supply chain transparency, security, and traceability by creating tamper-proof digital records of transactions and materials.

Benefits of Smart Manufacturing
Get to know some of the major benefits of smart manufacturing:
- Efficiency and Productivity: Smart manufacturing streamlines operations through automation, real-time monitoring, and data-driven decision-making, leading to faster production and reduced waste.
- Agility and Responsiveness: Advanced technologies enable manufacturers to quickly adapt to market demands, supply chain disruptions, and shifting customer preferences.
- Sustainability: Optimized resource usage, energy-efficient processes, and waste reduction make smart manufacturing more environmentally friendly and cost-effective.
- Enhanced Supply Chain Visibility: Real-time data tracking and predictive analytics provide manufacturers with greater transparency across the supply chain, enabling better inventory management, faster issue resolution, and improved coordination with suppliers.
- Workplace Safety: Automation, robotics, and AI-driven monitoring help reduce human exposure to hazardous tasks, minimizing workplace injuries and creating a safer, more efficient manufacturing environment.
- Improved Quality Control: AI-powered monitoring and predictive analytics enhance product consistency, detect defects early, and minimize errors in production.
- End-to-End Savings: By reducing downtime, improving resource allocation, and minimizing material waste, smart manufacturing lowers operational costs and maximizes profitability.
Smart Manufacturing Disadvantages
Of course, with any new process or technology, there are going to be some setbacks. These are several disadvantages of smart manufacturing (which can all be managed with proper planning and top-tier technological partners and products):
- Upfront Cost of Implementation: Investing in advanced technologies, automation, and infrastructure upgrades can be expensive, making adoption challenging for smaller manufacturers.
- Complexity of Integration with Legacy Systems: Many factories rely on outdated equipment, and integrating smart manufacturing technologies with existing systems can be complicated and costly.
- Potential Cybersecurity Risks in Smart Factories: As factories become more connected, they are increasingly vulnerable to cyber threats, requiring robust security measures to protect sensitive data and operations.
- The Learning Curve and Training Needs for New Technologies: Employees must be trained to work with smart manufacturing for AI, IoT, and other advanced systems, which can take time and require significant investment in workforce development.
Smart Manufacturing Use Cases
Your team can integrate smart manufacturing in the following ways:
Predictive Maintenance
Predictive maintenance leverages IoT sensors and AI-driven analytics to monitor equipment health in real time, detecting early signs of wear and potential failures. By predicting when maintenance is needed, manufacturers can prevent costly downtime, reduce repair expenses, and extend machine lifespan. This proactive approach ensures that production runs smoothly without unexpected breakdowns, significantly improving overall efficiency.
Agile Production
Smart manufacturing enables agile production by allowing manufacturers to rapidly adjust production lines in response to market demands, supply chain disruptions, or custom orders. Advanced automation, digital twins, and real-time data analytics help manufacturers shift between product variations with minimal downtime. This flexibility is particularly beneficial in industries like automotive, electronics, and consumer goods, where demand fluctuations require quick adaptations.
AI-Driven Quality Inspection
AI-powered quality inspection systems use computer vision, machine learning, and high-speed cameras to detect defects with greater accuracy than traditional human inspections. These smart systems identify even the smallest inconsistencies in real time, ensuring that only high-quality products move forward in production. By minimizing defects and reducing waste, AI-driven quality control enhances product reliability and customer satisfaction.
Supply Chain Optimization
Smart manufacturing technologies enhance supply chain management by providing real-time visibility, predictive analytics, and automation to optimize logistics and inventory levels. Blockchain ensures secure, transparent transactions, while AI predicts demand fluctuations to prevent stock shortages or overproduction. This level of optimization helps manufacturers reduce costs, improve delivery times, and enhance supplier coordination, making operations more resilient.
Robotics Automation
Advanced robotics play a crucial role in smart manufacturing by automating repetitive tasks, increasing production speed, and improving workplace safety. Collaborative robots (cobots) work alongside human employees, handling dangerous or strenuous activities, while AI-powered robotic arms improve precision and efficiency. Robotics automation not only reduces labor costs but also enables factories to operate 24/7 with minimal errors, driving higher productivity and output.
Conversational AI for Smart Manufacturing
Another major component of successful manufacturing processes is communication. With conversational AI technology, like aiOla, your team can streamline manufacturing protocols and procedures using AI that generates human-like interactions.
Whether a team member has a question, needs additional training materials, or wants to convert speech into text, aiOla provides instant, accurate responses and seamless documentation across any language, jargon, accent, or acoustic setting.
By enabling hands-free, voice-activated workflows, conversational AI helps operators access critical information without disrupting their tasks. It also enhances collaboration across teams, reduces miscommunication, and improves overall efficiency. With real-time language processing and integration into existing systems, aiOla ensures that manufacturing facilities operate smoothly, reducing downtime and enhancing productivity.
Final Thoughts
Smart manufacturing is an integral part of the current state of manufacturing and will continue to evolve and innovate as new technologies emerge. Using AI for smart manufacturing not only helps your team be more efficient, but it also enhances decision-making, improves overall product quality, and reduces operational costs.
Smart manufacturing also lowers the risk of lost time, wasted resources, and, most importantly, workplace injuries by automating hazardous tasks. There are many ways to integrate smart manufacturing into your business, from predictive maintenance to robotics automation, helping you keep up with consumer demands, production goals, and the ever-changing market landscape.


